Section 6. 자바스크립트 String 객체
I. 생성자 함수
const strObj1 = new String();
const strObj2 = new String('Hello World!');
console.log(strObj1);
console.log(strObj2);strObj1과 strObj2의 출력을 비교하면 다음과 같다.
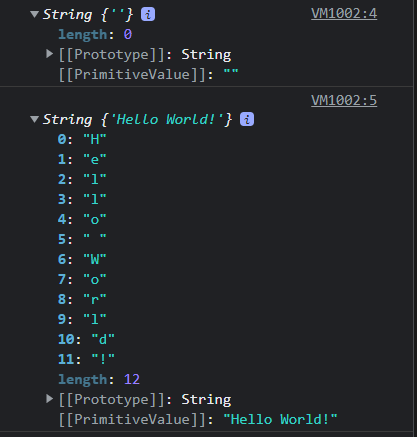
PrimitiveValue가 다른 것을 확인 할 수 있다. 또한 여기서 문자열도 유사배열 객체인 것을 확인 가능하다.
console.log(strObj1.valueOf(), strObj1.toString()); //
console.log(strObj2.valueOf(), strObj2.toString()); //Hello World! Hello World!valueOf 또는 toString 메서드는 해당 문자열의 원시값을 반환한다.
const fromNum = new String(123);
const fromBool = new String(true);
const fromArr = new String([1, 'A', false]);
const fromObj = new String({a: 1});
console.log(typeof fromNum, fromNum); //object String {'123'}
console.log(typeof fromBool, fromBool); //object String {'true'}
console.log(typeof fromArr, fromArr); //object String {'1,A,false'}
console.log(typeof fromObj, fromObj); //object String {'[object Object]'}다른 타입들도 감쌀 수 있는 것을 확인 할 수 있다. 문자열로 변호나한 값을 가진 String 객체를 반환한다.
추가적으로 new 없이 사용하면?
const str1 = String('Hello World!');
const str2 = String(123);
const str3 = String(true);
const str4 = String({x: 1, y: 2}); // 💡 [object Object]
const str5 = String([1, 2, 3]); // 💡 1,2,3
console.log(typeof str1, str1); //string Hello World!
console.log(typeof str2, str2); //string 123
console.log(typeof str3, str3); //string true
console.log(typeof str4, str4); //string [object Object]
console.log(typeof str5, str5); //string 1,2,3생성자로서가 아닌 String 함수는 주어진 인자를 문자열로 변환하여 반환한다.
II. 유사 배열 객체
let myStr = '안녕하세요!';
console.log(
myStr.length,
myStr[0],
myStr[myStr.length - 1]
); //6 '안' '!'
myStr[myStr.length - 1] = '?';
console.log(myStr); //안녕하세요!
for (const letter of myStr) {
console.log(letter);
}
//안
//녕
//하
//세
//요
//!두번째 단락에 있는 코드를 보면 myStr의 마지막 요소를 ?로 바꿨는데 막상 출력을 해보면 바뀌지 않은 것을 볼 수 있다.
이유는 String은 원시값이기 때문이다. 즉, 배열처럼 접근하는 방식으로는 수정이 불가능 하다는 뜻이다. 굳이 수정하려면 변수 값 자체를 다른 문자열로 대체해야 한다.
정리하자면 다음과 같다.
- length 프로퍼티 : 글자 수 반환한다
- [ ] 안에 인덱스 숫자를 넣어 ~번째 글자 읽기(만) 가능하다
- for ... of문 사용가능. 이터러블이기 때문이다
III. 주요 인스턴스 메서드
1. toUpperCase, toLowerCase
라틴어 문자를 모두 대문자/소문자로 변경하여 반환하는 메서드이다.
const word = 'Hello, World.';
console.log(
word.toUpperCase(),
word.toLowerCase()
); //HELLO, WORLD. hello, world.
console.log(word); //Hello, World.기존의 문자열은 바꾸지 않는다는 점이 포인트이다. 그리고 이 아래에 소개되는 메서드들도 마찬가지이다.
2. charAt, at
인자로 주어진 인덱스의 문자를 반환하는 메서드이다.
charAt 메서드 예시는 다음과 같다.
console.log(
'Hello World!'.charAt(0),
'안녕하세요~'.charAt(2)
); //H 하
at 메서드 예시는 다음과 같다.
console.log(
'안녕하세요~'.at(1),
'안녕하세요~'.at(-1)
); //녕 ~신기능이고 배열에서도 사용가능하다.
음수로 뒤에서부터 접근 가능한 것을 볼 수 있다(-1부터).
3. indexOf, lastIndexOf
indexOf는 인자로 주어진 문자열이 앞에서 처음 나타나는 인덱스를 반환한다.
lastIndexOf는 인자로 주어진 문자열이 앞에서 부터 가장 마지막으로 나타나는 인덱스를 반환한다.
포함되지 않을 시 -1을 반환한다.
const word = '반갑습니다!';
console.log (
word.indexOf('습'),
word.lastIndexOf('습')
); //2 2
4. includes, startsWith, endsWith
인자로 주어진 문자열을 포함 (아무곳에/ 맨 앞에/ 맨 끝에) 여부를 불리언으로 반환하는 메서드이다.
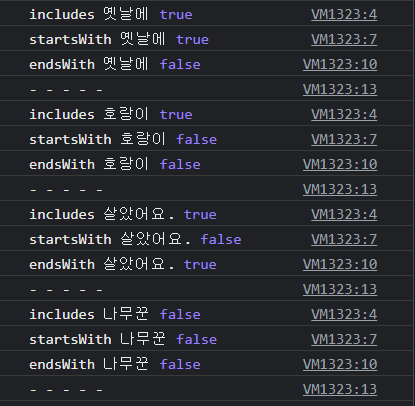
const sentence = '옛날에 호랑이 한 마리가 살았어요.';
for (const word of ['옛날에', '호랑이', '살았어요.', '나무꾼']) {
console.log(
'includes', word, sentence.includes(word)
);
console.log(
'startsWith', word, sentence.startsWith(word)
);
console.log(
'endsWith', word, sentence.endsWith(word)
);
console.log('- - - - -');
}출력문은 다음과 같다.
5. search
인자로 받은 정규표현식과 일치하는 첫 부분의 인덱스를 반환하는 메서드이다.
없을 시 -1을 반환한다.
console.log(
'하루가 7번 지나면 1주일이 되는 거야.'.search(/[0-9]/),
'하루가 일곱 번 지나면 일주일이 되는 거야.'.search(/[0-9]/)
); //4 -1
6. substring
인자로 전달받은 인덱스(들)을 기준으로 자른 문자열을 반환하는 메서드이다.
const word = 'ABCDEFGHIJKL';
const part = word.substring(4, 8)
console.log(word, part); //ABCDEFGHIJKL EFGH
console.log(
word.substring(-1),
word.substring(4, 100),
word.substring(100)
); //ABCDEFGHIJKL EFGHIJKL인자를 하나만 넣으면 해당 인덱스부터 끝까지 반환한다.
음수나 범위 외 숫자는 범위 내 최소/최대 숫자로
7. slice
substring과 같으나 음수로 뒤에서부터 자를 수 있는 메서드이다.
const word = 'ABCDEFGHIJKL';
console.log(
word.substring(-4),
word.slice(-4)
); //ABCDEFGHIJKL IJKL
8. split
인수로 주어진 문자열이나 정규표현식으로 분리하여 배열을 반환하는 메서드이다.
console.log(
'010-1234-5678'.split('-'),
'ABC1DEF2GHI3JKL'.split(/[0-9]/)
)
// ['010', '1234', '5678']
// ['ABC', 'DEF', 'GHI', 'JKL']// 인자로 빈 문자열을 넣거나 인자 생략시
const word = '안녕하세요';
console.log(
word.split(''),
word.split()
)
// ['안', '녕', '하', '세', '요']
// ['안녕하세요']const word = '하나 하면 할머니가 지팡이 짚고서 잘잘잘';
console.log(
word.split(' ', 2),
word.split(' ', 4)
)
//['하나', '하면']
//['하나', '하면', '할머니가', '지팡이']두 번째 인자로 배열의 최대 길이 지정이 가능하다.
9. trim, trimStart, trimEnd
앞뒤의 공백 제거하여 반환하는 메서드이다.
const word = ' Hello World! ';
console.log(`--${word}--`); //-- Hello World! --
console.log(`--${word.trim()}--`); //--Hello World!--
console.log(`--${word.trimStart()}--`); //--Hello World! --
console.log(`--${word.trimEnd()}--`); //-- Hello World!--중간의 공백은 제거하지 않는다.
10. repeat
인자로 주어진 정수만큼 문자열을 반복하여 반환하는 메서드이다.
const word = '호이';
console.log(word.repeat(3)); //호이호이호이
console.log(word.repeat(0)); //
console.log(word.repeat()); //
console.log(word.repeat(-1)); //애러인수가 없거나 0이면 빈 문자열을 반환하고 음수면 오류를 발생시킨다.
11. replace, replaceAll
첫 번째 인자로 받은 문자열 또는 정규식을 두 번째 인자로 치환한 결과를 반환하는 메서드이다.
console.log(
'이스탄불은 터키의 수도이다.'.replace('터키', '튀르키예')
); //이스탄불은 튀르키예의 수도이다.const word = '철권은 최고의 게임이다. 철권 대회 준비한다.';
console.log(word.replace('철권', '와우')); //와우은 최고의 게임이다. 철권 대회 준비한다.replace 의 첫 인자가 문자열이면 일치하는 첫 부분만 치환한다.
모두 치환하려면 정규식 /.../g 를 사용한다.
console.log(word.replaceAll(/철권/g, '와우')); //와우은 최고의 게임이다. 와우 대회 준비한다.replaceAll 은 문자열도 자동으로 /.../g 처럼 인식한다.
메서드 체이닝 method chaining
값을 반환하는 인스턴스 메서드를 연속으로 사용하는 것을 말한다.
const word = ' 모두 HELLO! ';
const rpFrom = 'hello';
const rpTo = 'bye';
console.log(
word
.trimStart() // '모두 HELLO! '
.toLowerCase() // '모두 hello! '
.replaceAll(rpFrom, rpTo) // '모두 bye! '
.toUpperCase() // '모두 BYE! '
.repeat(3) // '모두 BYE! 모두 BYE! 모두 BYE! '
.trimEnd() // '모두 BYE! 모두 BYE! 모두 BYE!'
); //모두 BYE! 모두 BYE! 모두 BYE!
console.log(word); //모두 HELLO!원본은 그대로인 것을 확인하고 넘어가자.